The processes are; PRACTICAL, TECHNICAL, ECONOMICAL
e.g. Rotary, Digital, Screen, Pad Printing
Reper Graphics - preparing the set up to prepaire to print - take artwork, checks the colour, position and technical issues
That then goes to the prink making to create the finished product
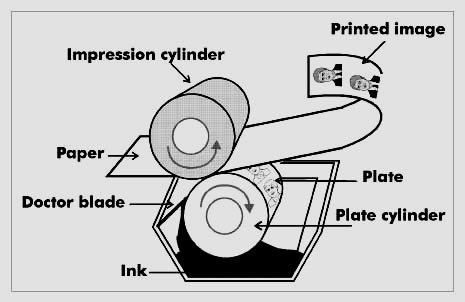
LITHO PRINTING - Rotary - SMALLER, but QUALITY job e.g. leaflets, mailshots, comics etc
- It is a ROTARY type of printing - it goes round, The image printing places are wrapped around the cyliners
- Printed fed onto sheet/roll
- There are 3 types
- Offset Lithography
- Rotogravure
- Flexography
- The sheets are etched - chemical process
- some places have DTP - meaning there are no sheets involved
- PDF goes straight to the plate
- Made sure BEFORE it goes to the plate that you check and get all the information right because if you notice after it will be a very expensive mistake, this is called the PROOF PROCESS
- a big proportion of the job cost is simply just setting up the equipment/machines, which can take up to half a day/whole day
- examples of this kind of print;
- increadibly high speed and runs on rolls of material as opposed to sheet fed.
- they often have the finish/folding/cut out etc included in the machine process
RETROGRAVURE (GRAVURE) - Mass Production
- Much more sturdy plate - so can produce more and the relief is deeper so the product is more durable
- hold more ink
- copper plates with mirror image so that it goes straight from PLATE to PAGE
- Typical GRAVURE print = lino print floor which are high volume and durable
- Its really to do with the NUMBER = high number produced and the products last for a long time
FLEXOGRAPHY (FLEXO) - for PACKAGING
- It is a POSITIVE mirror image rubber polymer plate, on a cylinder
- Rubber plate, 2 mm raised, can feel the relief
- The quality ISN'T as good as the litho print
- Prints = crisps, cellophane, stretchy material
- silicon feel, usually roll feed
RECAP
- LITHOGRAPHY (LITHO) = PLANOGRAPHIC - aluminium plate
- ROTOGRAVURE (GRAVURE) = INTAGLIO - copper plate
- FLEXOGRAPHY (FLEXO) = RELIEF - rubber plate
DIGITAL PRINTING e.g. BILLBOARDS
- The reproduction of image by translating the digital code direct from a computer to a material without intermediate physical process
- You have to consider; material its printed on to, the ink, the layout
- You are completely in charge of this every step of the way UNLIKE all the other processes of printing
- e.g. you collect printer, you can do a MOCK UP and show examples of work before sending it to print
- 'R.I.P' - 'RASTA IMAGE PROCESSOR' - it takes the computer code and works it out according to the certain printer
- Digital printing is IDEAL suited to short run/specials on a range of print media from paper to material.
SCREEN PRINTING e.g. T-SHIRTS (quality and durable)
- Printing technique which uses WOVEN blocks
- Hand or Mechanical
- Mechanical process - each screen has a different colour on it, the number of screens depends on the number of colours going onto the product
- ROTARY SCREEN PRINTING - the results are really durable
- The DIGITAL printing has taken over SCREEN printing
COLOUR SYSTEMS
SUBTRACTIVE COLOUR - Ink
- The more colour you lay on top, the less light is reflected (darker) so the colours are subtracted and it becomes dark
ADDITATIVE COLOUR - Screen
- The reverse of subtractive colour, the MORE colour you mix together, the lighter it becomes until it is white
VISIBLE GAMUT
This is all the colours in the world on a spectrum, there are many more colours that we see on screen but we cant print them
Look at the comparisons of RGB to CMYK
ARTWORK, COLOUR MODELS, LIMITATION
DEFINITIONS
CMYK (cyan/magenta/yellow/key black – 4 colour process) Subtractive.
This is used in the most common printed process called litho or offset litho RGB (red/green/blue – screen based) Additive.
Greyscale (Black and white continuous tone and any shade of grey, such as a black and white photograph)
Duotone (when a continuous tone image is printed in 2 or more spot colours – this term is also generally used when describing tri and quadtones.
Spot colour (one or more specially mixed colours as opposed as a result of a CMYK or RGB mix)
Mono (like greyscale but with a coloured ink, ie: one colour and percentage tints of that colour, plus the colour of the material it’s printed on
USEFUL LINKS
LITHO PRINTING
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XUlBueqStg4PAZZAZ RANT
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VpAuDrs5ocgPAD PRINT
http://www.pdsconsulting.co.uk/2007/Library/Printing_Pad.asp
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RlypyjjLDZI&feature=related
SCREEN PRINT
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YFM_tBfyjM0http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=i3iY21z8qLQ&feature=related
COLOUR http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=059-0wrJpAU&feature=relmfu CMYK and printing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TUd4r5olX1Q&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8cOZv4AF4pc&feature=related CMYK v RGB http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fNisT6ROdUo&feature=related RICH BLACK Vs NORMAL http://marvin.mrtoads.com/richblack_vs_plainblack.html
ABOUT PANTONE http://www.youtube.com/watch?gl=NL&hl=nl&v=l6r_CK0rNlk ABOUT COLOUR MATCHING http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pz3AMwRJiRw&feature=related COLOUR MODELS
http://www.sketchpad.net/basics4.htmhttp://www.devx.com/projectcool/ Article/19954













No comments:
Post a Comment